Types of Artificial Intelligence in 2026
Introduction of AI
Artificial intelligence is something that is made by humans or non-natural things, and intelligence means the ability to understand or think and learn and do the work. AI is not a system, but it is implemented in the system. There are many different types of AI, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Artificial Intelligence, or AI, is like teaching computers to think and act smart, just like humans—but much faster. Imagine a robot that can answer questions, a phone that recognizes your face, or a game that knows how you play and adjusts itself. That’s AI at work.
AI is when machines are made with intelligence smart enough to learn, decide, and help us. They don’t have brains like humans, but they use data, rules, and learning to act intelligently.
Types of Artificial Intelligence in 2026 will explore these categories, breaking down AI into three primary types based on capabilities and four types based on functionalities.
Why Is AI Important in 2026?
In 2026, AI is everywhere. It’s in engineering fields, schools, colleges, homes, markets, police operations, designs, hospitals, games, cars, airplanes, robots, and even cartoon robots. Kids today grow up talking to AI like it’s normal. AI helps people save time, learn better and best, and solve big and critical problems.
AI Today and in 2026
Now in 2026, AI can do so many things:
Talk like friendly humans and give any questions or anything.
Draw pictures for images.
Write stories for anything for blogs.
Drive a car. buses, trains, airplanes, and hovercraft.
Help kids learn lessons.
AI has grown from a small seed into a powerful big tree.
How Scientists Classify and Divide Artificial Intelligence
Scientists group AI into types to understand how smart it is and what it can do.
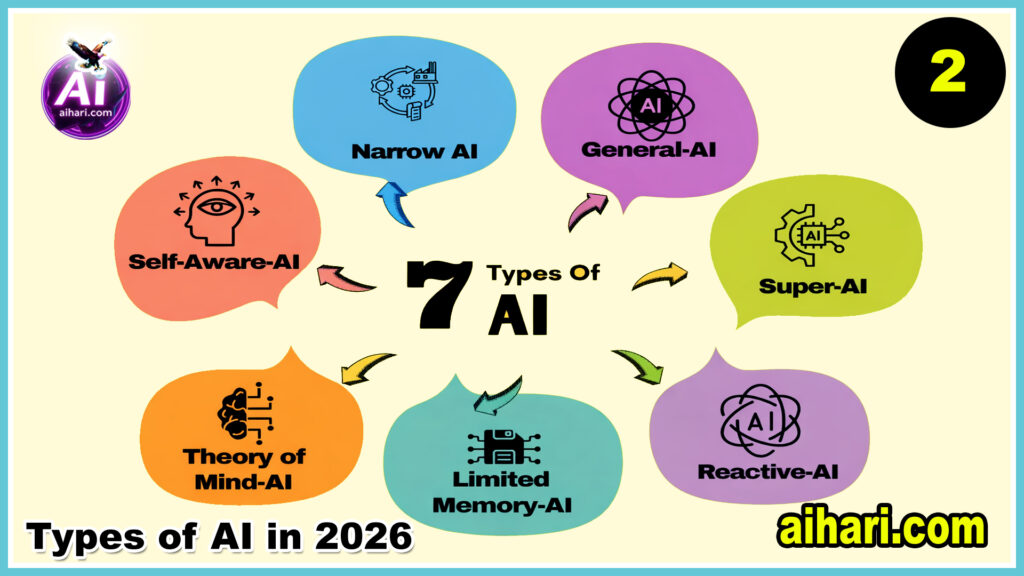
Types of Artificial Intelligence
The Types of Artificial Intelligence in 2026 blog states Artificial Intelligence (AI) has transformed industries, leading to significant advancements in technology, science, and everyday life. To understand AI better, we must first recognize that AI can be categorized into different types based on capabilities and functionalities.
Type 1: Based on Capabilities of AI (how powerful the AI is)
- Narrow AI
- General AI
- Super AI
Type 2: Based on the Functionality of AI (how the AI actually works)
- Reactive Machines
- Limited Memory AI
- Theory of Mind
- Self-Aware AI
Narrow AI—The Most Common AI in 2026
What Is Narrow AI?
Narrow AI is like a specialist teacher for a particular subject. A math teacher teaches math only, not science or art. Narrow AI is designed and trained on a specific task or a narrow range of tasks; narrow AI works the same way. This AI is better than humans.
| Brilliant at one thing, useless at everything else (Everything today) |
Examples of Narrow AI Kids See Every Day
- Alexa and Siri answer questions. Voice assistants that understand specific commands.
- Netflix suggesting cartoons
- AI in mobile games
- Spell check while typing on mobiles or computers.
- Facial recognition software is used in security systems.
- Recommendation engines are used by platforms like Netflix or Amazon.
General AI (Strong AI)
General AI systems that have human intelligence and abilities to perform various tasks. Systems have the capability to understand, learn, and apply across a wide range of tasks that are similar to how a human can adapt to various tasks.
| General AI is human-level across all domains (theoretical). It is completely theoretical. Does not exist anywhere. |
It could learn chess, then apply strategic thinking and learn business planning, then use both experiences to write a novel about competitive strategy.
Large language models (LLM) like ChatGPT appear general because they’re trained on diverse data, but they’re still narrow—they only process text. They can’t learn to drive a car or perform surgery.
- Robots that can learn new skills and adapt and do work to challenges in real time.
- AI systems that could autonomously diagnose and solve complex medical issues across various specializations in the hospitals.
Superintelligence (Super AI)
Super AI would be smarter than humans, doctors, scientists, and teachers combined.
Super AI is not real yet. It’s just a thought and an idea for the future.
Super AI surpasses the intelligence of humans in problem-solving, creativity, and overall abilities. Super AI develops emotions, desires, needs, and beliefs of their own. They are able to make decisions of their own and solve problems of their own. Such AI would not only be able to complete tasks better than humans but also understand and interpret emotions and respond in a human-like manner.
Types of Artificial Intelligence Based on Functionalities
Reactive Machines
Reactive AI reacts only to what is happening at present now. It is not focused on past works; it does not remember the past.
How it works:
Pure input → processing → output.
No memory of previous interactions or learning from past experiences.
Examples:
- Spam filters: Analyze email content and classify as spam or legitimate
- Basic recommendation systems: “People who bought A also bought B and C….”
- Simple image recognition: Identify objects in photos without learning preferences
- Customer service chatbots: Respond to keywords without conversation context.
Limited Memory AI—The Learning Machine
How it works:
Uses historical data and past experiences to inform current decisions. Can improve performance through training and experience.
The “memory” is actually training data and recent interactions, not true episodic or long-past memory like humans have.
Examples:
Large Language Models (ChatGPT, Claude):
- Trained on massive text datasets
- Use conversation history for context
- Generate responses based on patterns learned from training
Self-driving cars:
- Learn from millions of driving scenarios
- Improve navigation based on traffic patterns
- Adapt to different road conditions and weather
Image recognition systems:
- Trained on millions of labeled photos
- Recognize faces, objects, and scenes
- Improve accuracy as they process more data
Recommendation engines:
- Netflix analyzing your viewing history and preferences
- Amazon suggesting products based on purchase patterns
- Spotify creating personalized playlists from listening habits
- Chatbots that can remember recent conversations to improve the flow and relevance of replies.
Theory of Mind AI—The Empath (Theoretical)
AI that understands human emotions, motivations, intentions, and beliefs. It could predict how people will react and personalize interactions based on individual psychology.
Current research examples:
- Emotion recognition: AI analyzing facial expressions, voice tone, and body language
- Sentiment analysis: Understanding emotional context in text and social media
- Social robotics: Robots designed to interact naturally with humans
- Therapeutic AI: Early experiments in AI counselors and mental health support
- Human-robot interaction where AI could detect emotions and adjust its responses to empathize with humans.
- Collaborative robots that work alongside humans in fields like healthcare, adapting their tasks based on the needs of the patients.
Self-Aware AI—The Conscious Machine (Theoretical)
AI that understands its own existence, limitations, and goals. It would have genuine self-awareness, emotions, and personal motivations.
Philosophical implications:
Current reality: We don’t fully understand human consciousness, making artificial consciousness even more complex. This remains in the realm of philosophy and science fiction.
Ethical considerations: Self-aware AI would raise fundamental questions about the nature of consciousness, rights, and our responsibilities as creators.
How Functionalities Combine with Capabilities
Understanding both aspects reveals the complete picture:
|
Conclusion
The evolution of AI has led to advancements in various industries, from narrow AI systems that simplify daily tasks to the theoretical development of super AI. Understanding the different types of AI based on capabilities and functionalities provides a clearer picture of where we are in the AI journey and where we are heading. As AI research progresses, it’s crucial to explore the ethical and societal impacts of more advanced AI systems while continuing to harness their potential for innovation.